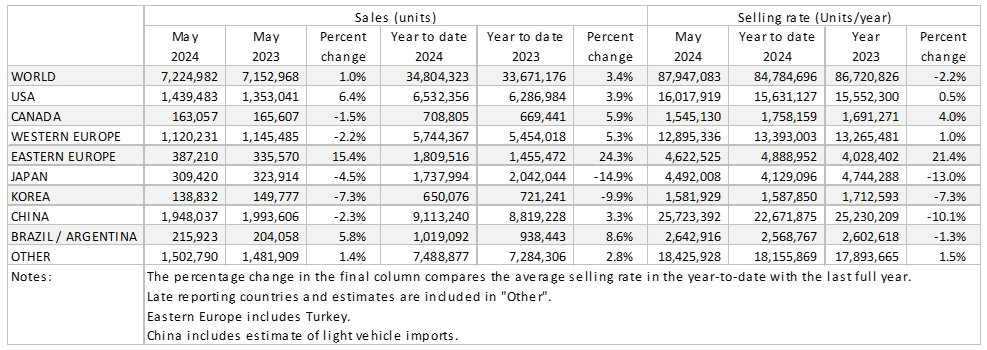
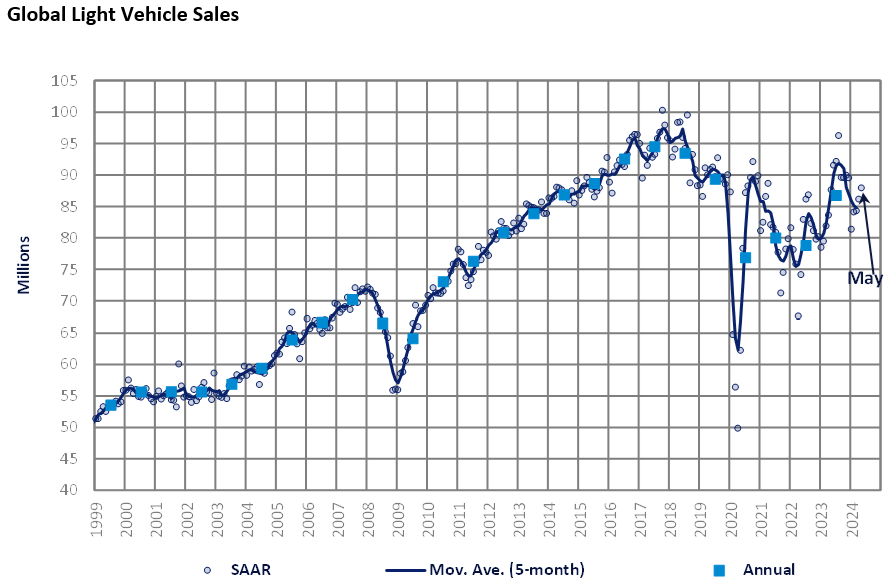
The Global Light Vehicle (LV) selling rate stood at 88 million units/year in May, a modest improvement on the previous month. With 7.2 million vehicles sold last month, this was a 1.0% improvement year-on-year (YoY), with year-to-date (YTD) sales up 3.4%.
Key markets, China and the US, benefited from improved selling rates versus the previous month. In Europe, there was little change for the West of the region in its MoM selling rate evolution, while Eastern Europe made progress, with the latter once again supported by recovery in Russia. In Japan, the selling rate declined notably as supply issues persist.
North America
The US Light Vehicle seems to be back on track following a contraction last month, as sales grew by 6.4% YoY in May 2024 to 1.44 million units, although an additional selling day compared to May 2023 provided a boost. The selling rate increased to 16.0 million units/year in May, up from 15.9 million units/year reported in April. Transaction prices slightly slowed in May, by US$66 MoM, bringing the value to US$44,813. Incentives continued to exceed the US$2,000 level for a seventh consecutive month, at US$2,689.
In May, Canadian Light Vehicle sales reached, 163.1k units, representing the first YoY reduction of 2024, as sales slowed by a marginal 1.5% YoY. Sales continue to battle economic headwinds, with the selling rate dropping to 1.5 million units/year in May, from 1.6 million units/year in April. Looking at Mexico, sales grew by a strong 13.5% YoY in May, to 120.7k units. With the Mexican economy showing signs of stability, allowing for LV sales to grow, the selling rate expanded in May 2024 to 1.52 million units/year, up from 1.50 million units/year recorded in April.
Europe
The LV selling rate for Western Europe stood at nearly 13 million units/year in May. In YoY terms, sales volumes were down 2% YoY with the market struggling due to persistent economic headwinds. We continue to forecast growth for the full year even though it will not match the YTD performance. On a positive note, the ECB cut rates in June, and with further cuts assumed, this should be more supportive for the economy generally, and automotive sales specifically, over the medium term.
The Eastern Europe LV selling rate increased MoM in May, with raw sales up by a double-digit percentage YoY. Strong sales continue to be driven by robust recovery in Russia. The Turkish LV market registered 100k units in May, a 10% decrease YoY, primarily driven by successive rises in interest rates by the Central Bank (CBRT).
China
According to preliminary data, China’s domestic market picked up some pace in May. The May selling rate was 25.7 million units/year, up 8% from April. That, however, brought the YTD average selling rate to only 22.7 million units/year. In YoY terms, sales (i.e., wholesales) declined by 2.3% in May, despite the government’s continued efforts to shore up the domestic automotive market. In contrast, Passenger Vehicle exports continued to expand by double digits.
Earlier this year the central government, along with local governments, launched a trade-in subsidy program, but that does not appear to have substantial positive impact on sales so far. Some larger cities have restrictions on new vehicle sales based on the traffic conditions, which has been an obstacle for sales. The price war continues, led by BYD, and BYD’s ultra-low prices are drawing criticism even from other Chinese OEMs. For consumers, however, increasing choices of attractive and affordable NEVs that suit their needs are a good development.
Other Asia
The Japanese market remains volatile, due to the ongoing supply issues. The May selling rate was 4.5 million units/year, down nearly 9% from a strong April. Sales declined by 4.5% YoY in May and 15% YTD, due partially to a high base, but mainly to Daihatsu and Toyota’s production suspension earlier this year. The new scandal has emerged at Toyota, Mazda, Honda and Suzuki over the government’s vehicle certification process, but we expect that its impact on sales will be very limited, as the issue is with the process, not with the vehicles themselves. A larger concern arises from sticky inflation and falling real wages that are eroding consumers’ purchasing power.
The Korean market remains sluggish, despite the fact that the economy rebounded strongly in Q1. The May selling rate was 1.58 million units/year, the second straight month of MoM decline. Light Commercial Vehicle (LCV) sales were particularly weak, continuing to fall YoY by double digits. Sales were impacted by high financing costs, aging LCV models, and the payback of the temporary tax cut on Passenger Vehicles last year. All Korean brands posted YoY decline in May, but sales of imported models expanded, led by strong deliveries by Tesla. Hyundai launched the China-built taxi-only Sonata, which contributed to growth of imports as well.
South America
Brazilian Light Vehicle sales continue to show strong growth in 2024, as sales grew by 9.8% YoY in May 2024, reaching 183.2k units. While sales were robust, the selling rate staggered in May to 2.27 million units/year, down from 2.41 million units/year recorded in April. Production struggled in May due to floods stemming from the Rio Grande do Sul. Inventory slightly declined to 237.5k units, down from 242.6k units in April, and days’ supply declined by 1 day on a month-over-month basis to 37 days.
In Argentina, Light Vehicle sales landed at 32.7k units in May, dropping by 12.0% YoY. Imported vehicles continue to expand following the removal of the import restrictions, as the increasing volume of these foreign-built vehicles are coming from Asian countries, harming Brazilian exports to Argentina. As the country grapples with economic uncertainty, the selling rate continues to fluctuate, dropping to 374k units/year in May, down from the 406k units/year reported in April.