The automotive industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by enhanced vehicle safety, autonomous vehicles, and connected vehicles, and the growing importance of technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. In the last three years alone, there have been over 1.2 million patents filed and granted in the automotive industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Automotive: Tyre belt layer compositions. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
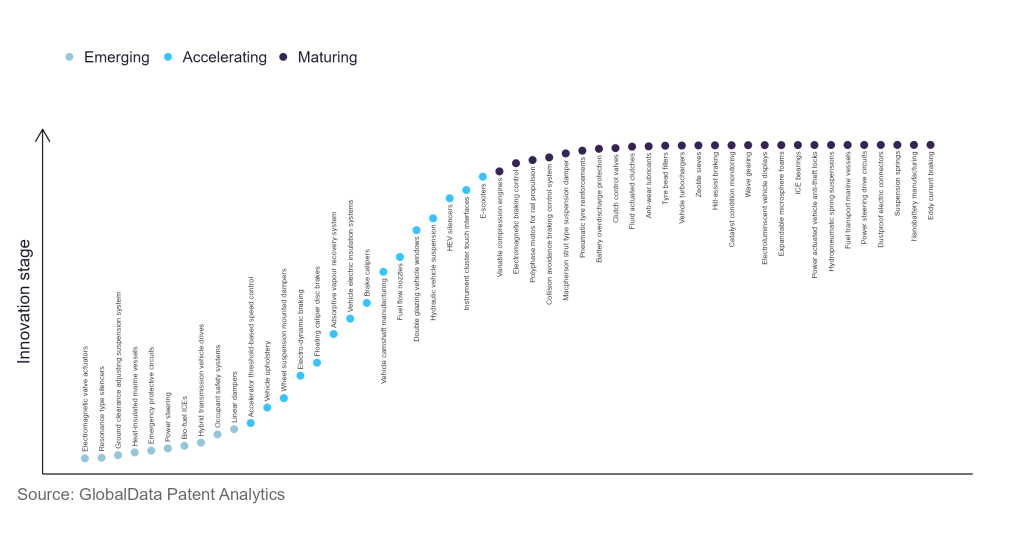
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
290+ innovations will shape the automotive industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the automotive industry using innovation intensity models built on over 619,000 patents, there are 290+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, resilient spoke wheels, auto-transmission lubrication circuits, and ignition switching engines are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Engine purge actuators, electro-dynamic braking, and adsorptive vapour recovery system estimation are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are collision avoidance braking control system and direct injection type engines, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for the automotive industry
Tyre belt layer compositions is a key innovation area in automotive
Tyre belts are made of rubber-coated layers of steel, fibreglass, rayon, and other materials situated between the tread and plies that crisscross at angles and hold the plies in place. Tyre belts provide resistance against punctures and help treads stay flat and in contact with the road.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 20+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established automotive companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of tyre belt layer compositions.
Key players in tyre belt layer compositions – a disruptive innovation in the automotive industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to tyre belt layer compositions
| Company | Total patents (2010 - 2022) | Premium intelligence on the world's largest companies |
| Compagnie Generale des Etablissements Michelin | 397 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Bridgestone | 318 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Sumitomo Electric Industries | 168 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Yokohama Rubber | 77 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Camfin | 65 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Goodyear Tire & Rubber | 58 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Continental | 41 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Kuraray | 26 | Unlock Company Profile |
| International Business Machines | 24 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Otsuka Holdings | 24 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Zeon | 19 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Sennics | 16 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Seino Holdings | 15 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Asahi Kasei | 13 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Milliken & Co | 13 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Hankook Tire & Technology | 12 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Haci Omer Sabanci Holding | 11 | Unlock Company Profile |
| LG | 11 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Trinseo | 11 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Kao | 10 | Unlock Company Profile |
| JSR | 9 | Unlock Company Profile |
| RAG-Stiftung | 8 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Toyo Tire | 8 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Mitsui Chemicals | 6 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Nippon Zeon | 6 | Unlock Company Profile |
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
Compagnie Generale des Etablissements Michelin is a key player in the tire belt layer compositions innovation area. Michelin’s tire belt layer compositions include rubber (natural rubber and synthetic rubber type), carbon black, metallic elements, textile and sulphur. The materials used are high-tech and the production processes interlock with millimetre and second precision. The use of high-tech materials also reduces the consumption of raw materials by an average of one-third. Michelin’s tire belt layer compositions protect the finished product against environmental influences such as ozone, UV rays and oxidation, while sulphur ensures the optimal bonding of the carbon black molecules during vulcanisation. Bridgestone, Sumitomo Electric Industries, Yokohama Rubber, and Goodyear Tire and Rubber are some of the other key players.
To further understand the key themes and technologies disrupting the automotive industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Automotive.
Premium Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.



