The automotive industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by electrification, low carbon emission technologies, and innovations in charging infrastructure and growing importance of technologies such as smart meters and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies. In the last three years alone, there have been over 1.2 million patents filed and granted in the automotive industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Internet of Things in Automotive: EV charging metering. Buy the report here.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
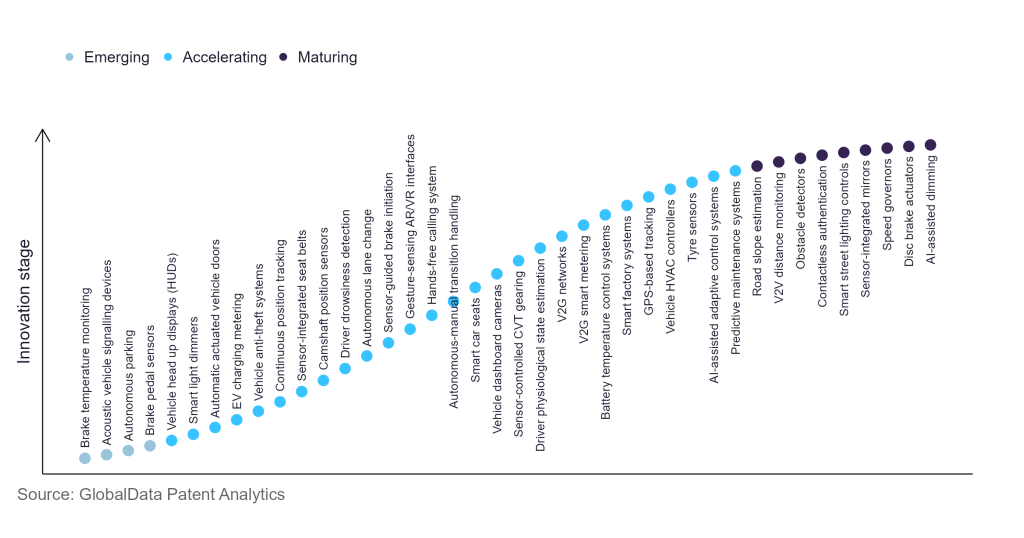
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
290+ innovations will shape the automotive industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the automotive industry using innovation intensity models built on over 619,000 patents, there are 290+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, smart car seats, tyre sensors, and predictive maintenance systems are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Acoustic vehicle signalling devices, brake temperature monitoring, and autonomous parking are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are disc brake actuators and AI-assisted dimming, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for IoT in the automotive industry
EV charging metering is a key innovation area in IoT
As electric vehicle (EV) owners refuel their electric cars' power supplies, many charging stations provided by high-use commercial or residential buildings can require a large amount of electricity. In situations like these, EV charging stations need to correctly measure their energy usage and costs.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 60+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established automotive companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of EV charging metering.
Key players in EV charging metering – a disruptive innovation in the automotive industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Toyota, Emerging Automotive and Gogoro are the leading patent filers in the EV charging meter segment. Toyota filed 91 patents. With more than 30,000 public stations supporting Level 2 and DC Fast Charging, Toyota is working on several solutions for billing meter for EV charging. Other companies that have filed patents in the same segment are Honda, E.ON, and AES to name a few.
To further understand how IoT is disrupting the automotive industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Internet of Things (IoT) in Automotive.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.





