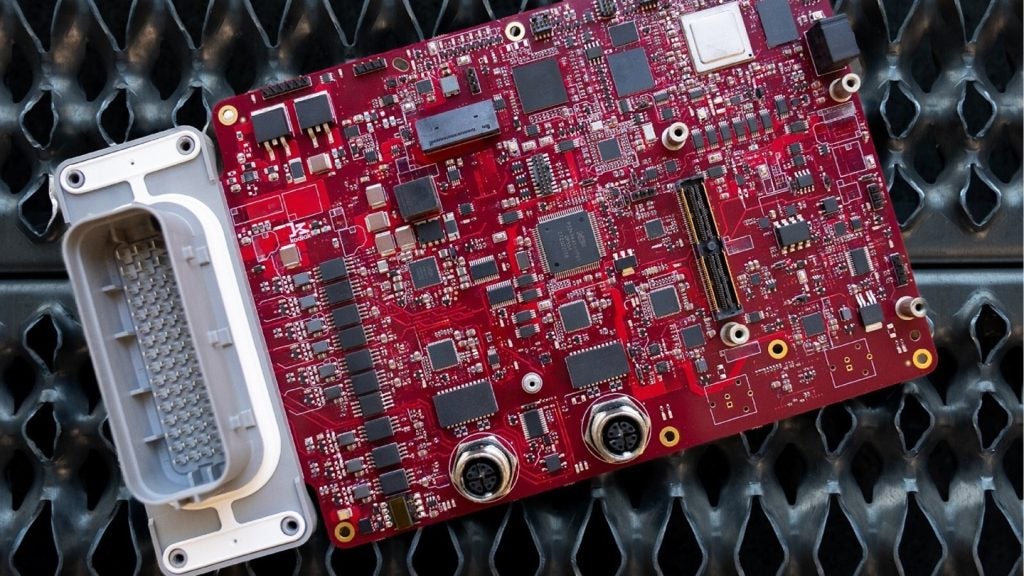
Japanese automaker Nissan Motor has joined forces with LiCAP Technologies, a US-based company, to advance the development of dry electrode production process technology for the next-generation electric vehicles (EVs).
The partnership will develop dry electrode production process technology for the cathode electrode of all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs), a critical component in the evolution of EVs.
This move comes as the company seeks to launch EVs with its in-house developed all-solid-state batteries by the fiscal year 2028, enhancing its research and development (R&D) activities to achieve this goal.
LiCAP's Activated Dry Electrode technology is anticipated to deliver improvements in production efficiency and battery performance.
The dry-process electrodes offer an advantage over traditional solvent-process electrodes by eliminating the requirement for drying and solvent recovery, thereby decreasing manufacturing expenses and lessening the impact on the environment.
Nonetheless, high production efficiency for mass production remains a significant hurdle for the adoption of dry-process electrodes.
Nissan noted that it started operations of its all-solid-state battery pilot line in January this year.
The company experienced a 5% drop in global sales to 262,133 vehicles in June. The sales downturn included a 3.7% decrease in Japan and a 5.1% reduction in overseas markets.
LiCAP Technologies is focused on advanced electrode manufacturing technologies. Furthering industry collaboration, it signed a letter of intent with battery cell manufacturer SK On in April.
This potential partnership aimed at exploring a strategic alliance to enhance lithium-ion battery electrode manufacturing, with the aim of utilising LiCAP’s Activated Dry Electrode technology to boost battery performance and cost efficiency for the next-generation EV battery cells of SKO.